- World Health Organization COVID-19 dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/
- Enria DA, Briggiler AM, Sanchez Z. Treatment of Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Antiviral Res. 2008;78(1):132-9.
- Enria DA, Briggiler AM, Fernandez NJ, Levis SC, Maiztegui JI. Importance of dose of neutralising antibodies in treatment of Argentine haemorrhagic fever with immune plasma. Lancet. 1984;2(8397):255-6.
- Hung IF, To KK, Lee CK, Lee KL, Chan K, Yan WW, et al. Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(4):447-56.
- Hung IFN, To KKW, Lee CK, Lee KL, Yan WW, Chan K, et al. Hyperimmune IV immunoglobulin treatment: a multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial for patients with severe 2009 influenza A(H1N1) infection. Chest. 2013;144(2):464-73.
- Mair-Jenkins J, Saavedra-Campos M, Baillie JK, Cleary P, Khaw FM, Lim WS, et al. The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211(1):80-90.
- Soo YO, Cheng Y, Wong R, Hui DS, Lee CK, Tsang KK, et al. Retrospective comparison of convalescent plasma with continuing high-dose methylprednisolone treatment in SARS patients. Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2004;10(7):676-8.
- Lai ST. Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;24(9):583-91.
- Cheng Y, Wong R, Soo YO, Wong WS, Lee CK, Ng MH, et al. Use of convalescent plasma therapy in SARS patients in Hong Kong. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2005;24(1):44-6.
- Arabi Y, Balkhy H, Hajeer AH, Bouchama A, Hayden FG, Al-Omari A, et al. Feasibility, safety, clinical, and laboratory effects of convalescent plasma therapy for patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection: a study protocol. Springerplus. 2015;4:709.
- Organization WH. Use of convalescent whole blood or plasma collected from patients recovered from Ebola virus disease for transfusion, as an empirical treatment during outbreaks. 2014 [Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/604045/retrieve.
- Dean CL, Hooper JW, Dye JM, Zak SE, Koepsell SA, Corash L, et al. Characterization of Ebola convalescent plasma donor immune response and psoralen treated plasma in the United States. Transfusion. 2020.
- Shen C, Wang Z, Zhao F, Yang Y, Li J, Yuan J, et al. Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with Covid-19 with convalescent plasma. JAMA 2020;323(16):1582–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4783.
- Duan K, Liu B, Li C, Zhang H, Yu T, Qu J, et al. Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2004168117.
- Ye M, Fu D, Ren Y, Wang F, Wang D, Zhang F, et al. Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol 2020. https://doi. org/10.1002/jmv.25882
- Ahn JY, Sohn Y, Lee SH, Cho Y, Hyun JH, Baek YJ, et al. Use of convalescent plasmatherapyintwoCOVID-19 patientswithacuterespiratory distresssyndrome in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2020;35:e149https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35. e149.
- Zhang Bin, Liu Shuyi, Tan Tan, Huang Wenhui, Dong Yuhao, Chen Luyan, et al. Treatment With Convalescent Plasma for Critically Ill Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Chest 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2020.03.039. In press.
- Points to consider in the preparation and transfusion of COVID-19 convalescent plasma. Jay Epstein & Thierry Burnouf on behalf of the ISBT Working Party on Global Blood Safety
- WHO Blood Regulators Network (BRN). Interim Position Paper on blood regulatory response to the evolving outbreak of the 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2*
- COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma Collection: Donor Eligibility, Processing, Labeling, and Distribution. AABB’s CCP collection protocol – 03 31 2020
- Centro Nazionale Sangue. Protocollo operativo per la selezione dei pazienti-donatori (convalescenti con diagnosi virologicamente documentata di COVID-19), per la qualificazione biologica del plasma da aferesi eventualmente prodotto nonché per le successive correlate procedure di riduzione dei patogeni e di stoccaggio controllato.
- "Position paper - SIMTI and SIdEM " on the production of hyperimmune plasma to be used in the therapy of SARS-CoV2 disease.
- Producción de plasma hiperinmune de donantes convalecientes COVID-19 (ConPlas-19). Multi-center, Randomized, Clinical Trial of Convalescent Plasma Therapy Versus Standard of Care for the Treatment of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients. Producción de plasma hiperinmune de donantes convalecientes covid-19, sometidos a un proceso de reducción de patógenos (inactivación).
- Protocole d’utilisation thérapeutique 24 avril 2020 Plasma convalescent COVID-19 Infection par le coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (maladie COVID-19)
- COVID-19 : L’ANSM encadre le recours possible à l’utilisation de plasma de personnes convalescentes pour des patients ne pouvant être inclus dans les essais cliniques - 30/04/2020
- Einfürung risikominimierender Massnahmem zur Prävention der Übertragungen des neuartigen Coronavirus (2019nCoV) durch Blutkomponenten zu Transfusion Empfehlung des Paul-Ehrlich-Instituts (PEI) vom (10.02.2020)
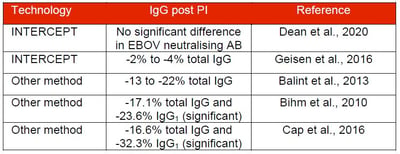
- Geisen et al., Pathogen-reduced Ebola virus convalescent plasma first steps towards standardization of manufacturing and quality control including assessment of Ebola-specific neutralizing antibodies, Vox Sanguinis, 2016
- Dean et al., Characterization of Ebola convalescent plasma donor immune response and psoralen treated plasma in the United States. Transfusion. 2020.
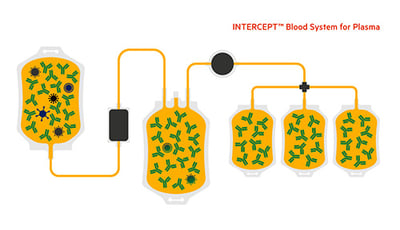
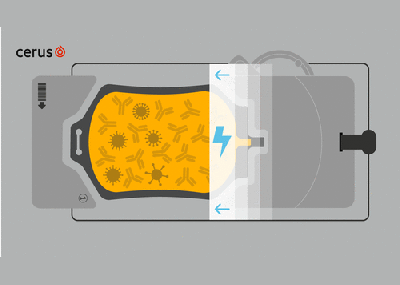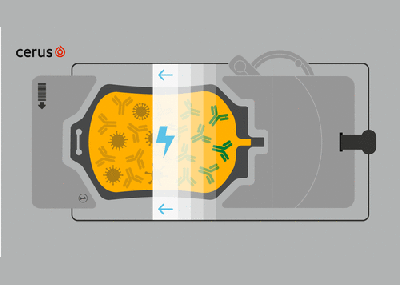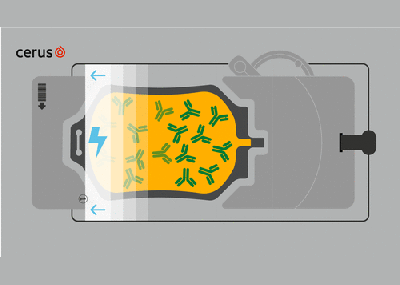
- INTERCEPT Blood System for Plasma, Technical Data Sheet
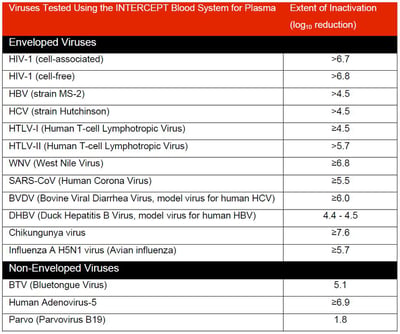
- Lanteri et al., Inactivation of a broad spectrum of viruses and parasites by photochemical treatment of plasma and platelets using amotosalen and ultraviolet A light, Transfusion 2020
- Singh et al., 2006. Photochemical treatment of plasma with amotosalen and longwavelength ultraviolet light inactivates pathogens while retaining coagulation function. Transfusion 46: 1168-1177
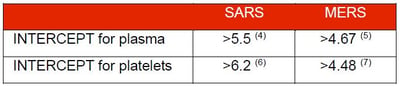
- Pinna et al., 2005. Amotosalen photochemical inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in human platelet concentrates. Transfus Med 15: 269-276
- Hindawi et al., 2018. Inactivation of Middle East respiratory syndrome-coronavirus in human plasma using amotosalen and ultraviolet A light. Transfusion 58: 52-59
- Hashem et al., 2019. Amotosalen and ultraviolet A light efficiently inactivate MERS-coronavirus in human platelet concentrates. Transfus Med 29: 434-441
- TUV approval
- Erickson A. et al., Plasma treated with amotosalen and ultraviolet A light retains activity for hemostasis after 5 days post-thaw storage at 1 to 6C, Transfusion, 2017
- INTERCEPT Blood System for Plasma, Instructions for Use
- Cerus data on file
- Theusinger O. et al., Quarantine versus pathogen-reduced plasma-coagulation factor content and rotational thromboelastometry coagulation, Transfusion, 2017